#sleep apena #snore #sleepcycle #well being
🌏 Related posts
💀 Death calculator : Predicting Life and Death
🥰 AGE-R Booster Healer: 5-Minute Home Skincare to Save on Dermatologist Visits
😎 Weight Loss with Wegovy and Ozempic: Side Effects and Ease of Use
🔆 How SONY Settles with the Heat Wave – Innovative Solutions for Scorching Weather
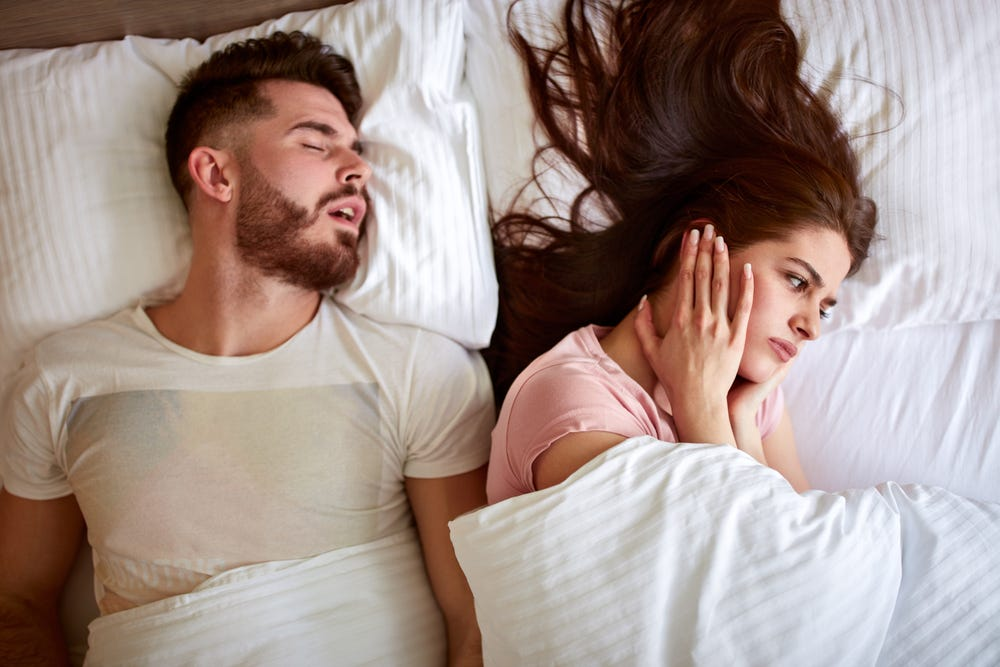

Snoring is a common issue affecting millions worldwide, and studies suggest that men are more prone to snoring than women. But why is this the case?
In this blog post, we’ll explore the underlying reasons for this gender difference, delve into the science behind snoring, and discuss sleep apnea, a related condition that can have serious health implications. We’ll also provide tips on how to manage snoring and improve sleep quality.
The Science Behind Snoring
Snoring occurs when the flow of air through the mouth and nose is partially blocked during sleep. This obstruction causes the tissues in the throat to vibrate, producing the characteristic sound of snoring. Several factors contribute to snoring, including the anatomy of the mouth and throat, sleeping position, and lifestyle habits.
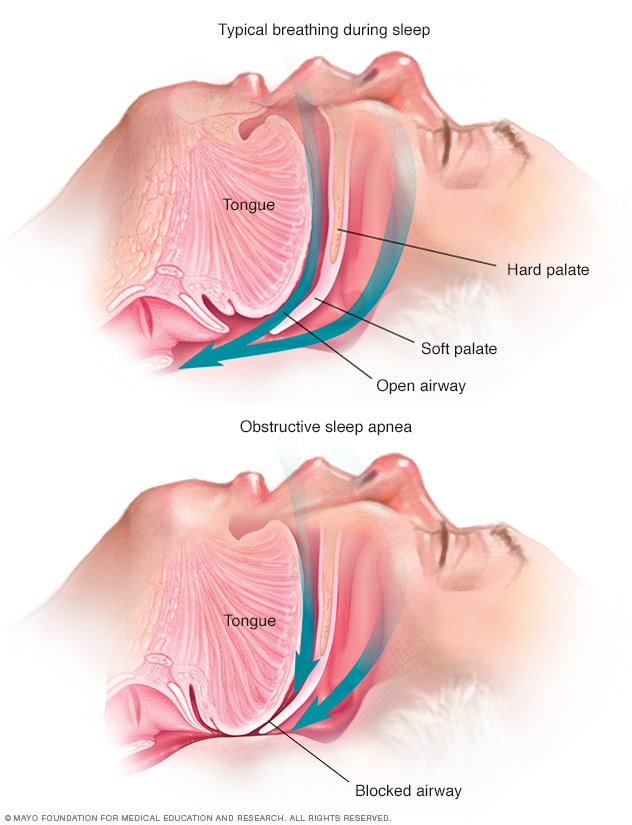
For men, certain anatomical features increase the likelihood of snoring. Men generally have narrower air passages compared to women, which can make it easier for these passages to become obstructed. Additionally, men tend to have larger necks, which can contribute to the collapse of the upper airway during sleep.
Hormonal Differences and Snoring
Hormones play a significant role in the differences between male and female snoring patterns. Estrogen and progesterone, hormones more prevalent in women, have protective effects on the upper airway, reducing the likelihood of airway collapse. These hormones help maintain muscle tone in the airway, preventing it from becoming obstructed during sleep.

However, as women age and reach menopause, the levels of these hormones decrease, which can lead to an increase in snoring and sleep apnea in older women. This shift highlights the importance of hormonal balance in maintaining healthy sleep patterns.
Sleep Apnea: A Serious Concern
While snoring can be a nuisance, it can also be a symptom of a more serious condition known as sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is characterized by repeated episodes of partial or complete blockage of the airway during sleep, leading to breathing pauses that can last from a few seconds to a minute or more. These interruptions in breathing can cause frequent awakenings, leading to poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue.

There are two main types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). OSA is the more common form and occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively, causing the airway to narrow or close. CSA, on the other hand, is related to the brain’s failure to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Men are at a higher risk of developing OSA due to the factors mentioned earlier, such as narrower airways and larger necks. Additionally, lifestyle factors like obesity, smoking, and alcohol consumption further increase the risk of sleep apnea in men.
Impact on Health and Well-Being
Untreated sleep apnea can have serious health consequences. It has been linked to a variety of conditions, including high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and depression. The repeated interruptions in breathing lead to decreased oxygen levels in the blood, putting a strain on the cardiovascular system.
Moreover, sleep apnea can lead to significant cognitive and psychological effects. Individuals with sleep apnea often experience memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and mood disturbances. The chronic fatigue associated with sleep apnea can also affect work performance and quality of life.
How Sleep Apnea Disrupts Your Sleepcycle and Why It Matters
Sleep apnea can significantly disrupt the natural sleep cycle, particularly the REM (Rapid Eye Movement) stage, which is essential for restorative sleep. During REM sleep, the muscles relax, and this relaxation can cause the airway to collapse more easily in people with sleep apnea, leading to frequent awakenings. These interruptions prevent the person from reaching deeper stages of sleep, resulting in poor sleep quality and excessive daytime fatigue. Continuous disruptions of the sleep cycle can also lead to long-term health problems, including cardiovascular issues and cognitive impairments. Managing sleep apnea effectively is crucial to restoring a healthy sleep cycle and overall well-being.
Managing Snoring and Sleep Apnea
Fortunately, there are several strategies to manage snoring and reduce the risk of sleep apnea. Lifestyle modifications are often the first line of defense. These may include:
- Weight Management: Losing excess weight can reduce fatty tissue in the throat, which can help open up the airway.
- Sleep Position: Sleeping on the side rather than the back can prevent the tongue from falling backward and blocking the airway.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Sedatives: These substances relax the muscles in the throat, increasing the likelihood of airway obstruction.
- Maintaining Regular Sleep Patterns: Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day can help regulate sleep and reduce the severity of snoring.
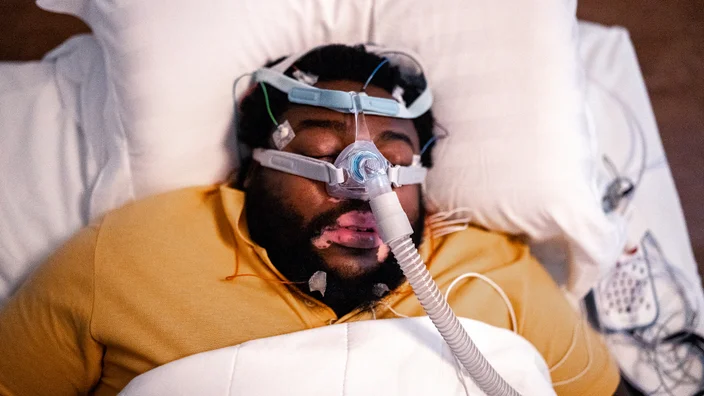
For those with moderate to severe sleep apnea, medical interventions may be necessary. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is a common treatment for OSA, involving the use of a machine that delivers air pressure through a mask to keep the airway open during sleep. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove or shrink the tissue that is blocking the airway.
Mewing: A Natural Technique to Alleviate Sleep Apnea
Mewing, a technique involving proper tongue posture and facial exercises, is gaining attention for its potential benefits in treating sleep apnea. By strengthening the muscles of the tongue and jaw, mewing can help maintain an open airway during sleep, reducing the risk of obstruction that causes snoring and apnea. This method encourages the tongue to rest against the roof of the mouth, which can promote better alignment of the jaw and improve overall breathing patterns, making it a promising adjunctive treatment for managing sleep apnea symptoms.
Gender Differences in Treatment and Management
The treatment and management of snoring and sleep apnea may vary between men and women. While the underlying mechanisms of the conditions are similar, gender-specific factors such as hormonal differences and anatomical variations can influence treatment outcomes.
For example, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be considered for postmenopausal women experiencing increased snoring or sleep apnea. HRT can help restore the protective effects of estrogen and progesterone on the airway muscles, potentially reducing the severity of the condition.
Additionally, women may be more responsive to lifestyle modifications than men. Studies have shown that women are more likely to adhere to weight management programs and make changes to their sleep habits, leading to better outcomes in reducing snoring and sleep apnea.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection and treatment of snoring and sleep apnea are crucial for preventing long-term health complications. It is important for individuals who snore regularly, particularly men, to seek medical evaluation if they experience symptoms such as excessive daytime sleepiness, loud snoring, gasping or choking during sleep, and difficulty concentrating during the day.
Sleep studies, also known as polysomnography, are often used to diagnose sleep apnea. These studies involve monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, including brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, and breathing patterns. The results of a sleep study can help determine the severity of sleep apnea and guide the appropriate treatment plan.
Conclusion: Taking Action for Better Sleep
Snoring and sleep apnea are more than just nighttime nuisances; they are serious health conditions that can have significant impacts on overall well-being. Understanding why men are more prone to these conditions than women is the first step in addressing the issue.
By taking proactive steps to manage snoring and seek treatment for sleep apnea, individuals can improve their sleep quality, reduce their risk of associated health problems, and enhance their quality of life. Whether through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, or a combination of both, there are effective strategies available to help both men and women achieve better sleep.
I encourage anyone who suspects they may have sleep apnea or is struggling with chronic snoring to consult with a healthcare provider. With the right approach, it is possible to overcome these challenges and enjoy the benefits of restful, restorative sleep.
답글 남기기